Skin injury is damage to the skin tissue that causes wound on the skin. Skin injuries often happen accidentally, but the wounds could range from minor to life-threatening. Minor wounds usually not serious and could be healed without complications, such as wounds caused by scratches, scrapes, cuts or tears; while the wounds might be life-threatening when the injuries lead to severe bleeding and infections, or the wounds were caused by strong chemicals, severe burn injury, or being bites by poisonous animals. Wound management is highly dependent on the types of wound, minor wounds could be healed with simple first aids, but serious and infected wounds required wound care and management by doctor or health professional.
Factors affect wound healing
Age: Elderly population age 60 years and above a have higher risk of impaired wound healing. Aging could affect wound healing when it is associated with altered inflammatory response, or impaired macrophage function, or decreased secretion of growth factors.
Stress: Stress causes delays in wound healing by affecting the hormone regulation in the body. Stress might up-regulate glucocorticoids which will influence immune cells, also reduce the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines at the wound, alter the inflammatory phase, and delay wound healing.
Diseases: Diabetes is one of the diseases that cause impaired wound healing. The impaired wound healing in diabetes involved hypoxia, dysfunction in fibroblast and epidermal cells, impaired angiogenesis, decreased host immune resistance, and neuropathy.
Medications: Medication which will interfere with blood clotting or platelet function, influence inflammatory response and cell proliferation would affect wound healing. The example of medications included glucocorticoid steroid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and chemotherapeutic drugs.
Alcohol consumption: Over-consumption of alcohol would cause ethanol intoxication and increase the risk susceptibility to infection. Alcohol exposure will suppress the release of the pro-inflammatory cytokine, decrease neutrophil and phagocytic function, increased the risk of post-injury infection.
Smoking: Tobacco smoke contains several substances that will cause negative effects on health and wound healing. Nicotine, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen cyanide from smoke are the substances that will affect wound healing. Nicotine has a vasoconstrictive effect, reduces tissue blood flow, causes tissue ischemia by restricting oxygen supply, and impaired wound healing.
Infections: The presence of microorganisms on the injured area will worsen wound healing. P.aeruginosa and Staphylococcus are the common bacteria in the infected and clinically non-infected wound, where these microorganisms cause impaired wound healing as it has resistant to conventional antibiotic treatment when occurred in the form of biofilm on the infected wound.
Wound management
First aid for cuts and scrape (minor wound):
- Wash hand and make sure the hands are clean before doing first aid.
- Stop the bleeding. Normally, a minor wound could stop bleeding immediately. However, if needed, apply gentle pressure with a clean bandage, cloth, or ice pack until the wound stops bleeding.
- Clean the wound. Rinse the wound with clean water, you may wash around the wound using soap, but do not get soap in the wound. After rinsing the wound, pat it dry with a clean towel.
- Apply ointment and wound dressing. Apply a thin layer of antibiotic ointment on the wound. Dress the wound properly by apply a bandage, rolled gauze, or gauze held in place with paper tape. Keep the dressing clean and dry. Change the dressing at least once a day, if the dressing gets wet or dirty, change the dressing immediately.
- Avoid scratching or rubbing the wound, do not remove scabs. If you have signs of infection such as increasing pain, warmth or swelling, on the skin or near the wound, visit doctor or health professional immediately.
First aid for minor burns:
- Cool the burn area using running water, cool pack, or wet compress until the pain eases.
- Remove jewelry or other tight items from the burned area before the area swells.
- Once the burn is completely cooled, apply lotion or moisturizer on it could help to relieve pain and prevent drying on the affected area. Home remedies such as aloe vera and raw honey can be applied on the affected area too. Honey has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties due to its high osmolarity, low pH, and enzymatic production of hydrogen peroxide from glucose.
- If there is blister after burn, do not break it. If the blister breaks, clean the area with water and apply antibiotic ointment.
- Cover the burn with a sterile bandage and wrap it loosely to avoid pressure on the affected area. Proper wound dressing could keep air off the affected area, reduce pain, and protect blistered skin.
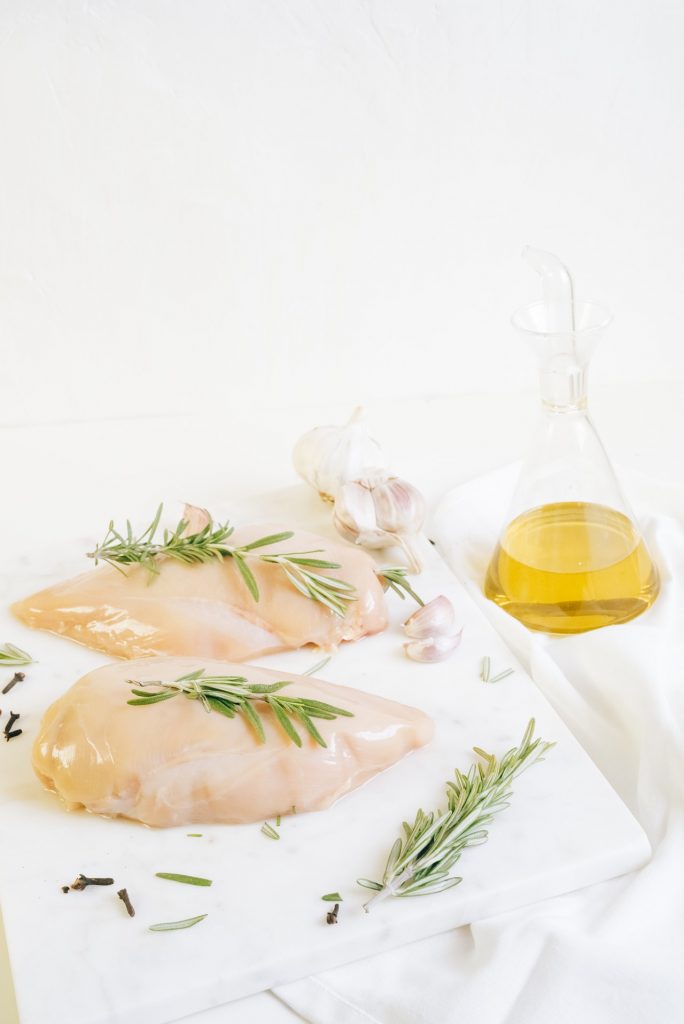

Nutrition for wound healing:
- Protein: Protein is an important nutrient for wound healing. It is essential for collagen synthesis, fibroblast proliferation, wound remodeling, and immune function. A high-quality protein often sources from a healthy protein food that does not contain salt, sugar, saturated fat, or extras that could negatively affect the body’s health. Examples of healthy protein sources include egg white, skinless chicken breast, Greek yogurt, fish, beans, and lentils.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3 fatty acids is essential for cell metabolism, gene expression, and angiogenesis in the wound site. It is well-known with anti-inflammatory properties and could improve immune function, reduce infectious complications. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids are egg yolk, fatty fish, flaxseed, walnut, caviar, soybean, etc.
3. Vitamins: Vitamins A (retinol), C (ascorbic acid) and E (tocopherol) have anti-oxidation and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Vitamin A has several biological properties, included anti-oxidation, increases fibroblast proliferation, increases collagen and hyaluronate synthesis, and modulates cellular differentiation and proliferation. The recommended intake for vitamin A is 900 mcg per day for men and 700 mcg per day for women. It can be obtained from foods such as carrot, sweet potatoes, pumpkin, beef liver, cheese, etc.
- Vitamin C has many roles in wound healing, it could influence collagen formation, immunomodulation, and tissue repair. Vitamin C deficiency causes impaired wound healing, affected immune response, and susceptible to infections. The recommended intake for vitamin C is 90 mg per day for men and 75 mg per day for women. Fruits and vegetables are always a good source of vitamin C, such as orange, kiwi, guava, tomato, broccoli, brussels sprout, etc.
- Vitamin E is widely promoted as an anti-scarring agent, it has anti-inflammatory properties and could lighten scar formation on the wound. It is also a fat-soluble antioxidant that could protect the cell from the damaging effects of free radicals. The recommended intake for vitamin E is 15 mg per day. It can be obtained through consumption of oil (olive oil, sunflower oil), seeds, nuts, avocado, olive, etc.

4. Minerals: Zinc, selenium, and iron are the essential micronutrients that have a beneficial effect in skin health maintenance. These minerals also play important roles in wound healing, such as reduce oxidative damage, modulate cell replication, tissue repair, and cell growth.
- Zinc is an essential mineral for cellular metabolism. It plays an important role in wound healing, immune function, protein synthesis, and cell division. The recommended intake for zinc is 11 mg per day for men and 9 mg per day for women. The foods rich in zinc are oyster, red meat, poultry, chickpea, beans, and nuts.
- Selenium is a trace mineral with anti-oxidative function, which could provide protection against oxidative damage and infection. The recommended intake for selenium is 55 mcg per day. The richest food sources of selenium are brazil nuts, seafoods, and organ meat, but you may also obtain zinc from grains and dairy products.
- Iron is an essential component of hemoglobin, which is a protein in red blood cells that carry oxygen from the lung to the body tissues. It is also important for cellular functioning and physical growth. The recommended intake of iron for men above 19 years old is 8 mg per day and women above 19 years old is 18 mg per day. The richest source of iron is red meat and seafood, you may also obtain iron from nuts, beans, vegetables, and fortified grain products.
GNE Gold-G® Health Food Series
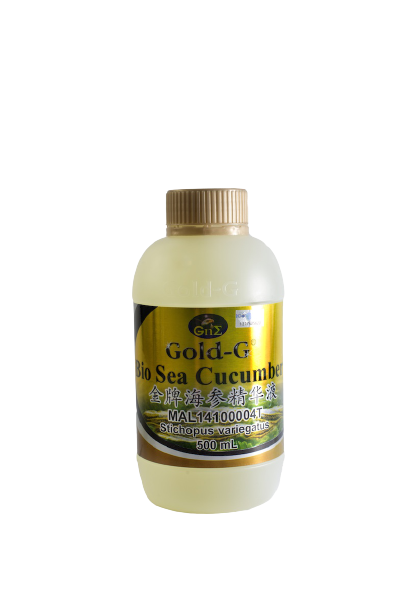
Gold-G® Bio Sea Cucumber
Sea cucumber is rich in pharmaceutical active components that provide beneficial effects on wound healing and promote healthy skin, such as collagen, mucopolysaccharides, peptides, and omega-3 fatty acids.
- Collagen promotes wound healing, repair damaged tissues, stimulates new blood vessels formation, and encourage the deposition of new collagen on the wound site.
- Mucopolysaccharides accelerate wound healing and improve wound concentration rate.
- Peptides in sea cucumber promote wound healing by reduce inflammation, improve angiogenesis and collagen deposition.
- Omega-3 fatty acids promote wound healing by initiating tissue repair ad reduce inflammation.
Gold-G® Gold Tualang Honey:
Tualang honey is raw honey harvested from Malaysia’s tropical rainforest. It is 100% pure and natural without undergo any additional treatment, hence it retained natural friendly bacteria, propolis, pollen grains, phytonutrients, phenolic acids and flavonoids. Besides natural taste and aroma, Tualang honey has higher nutritional value and stronger therapeutic effects than processed honey!
- Tualang honey possesses anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory effects, which could effectively reduce wound infections and improve wound healing especially for burns wound through an external application.
- Consumption of Tualang honey could help in maintaining healthy skin, reduce skin inflammation and protective effect against ultraviolet (UV) damage on skin due to its high phenolic content and antioxidants properties.
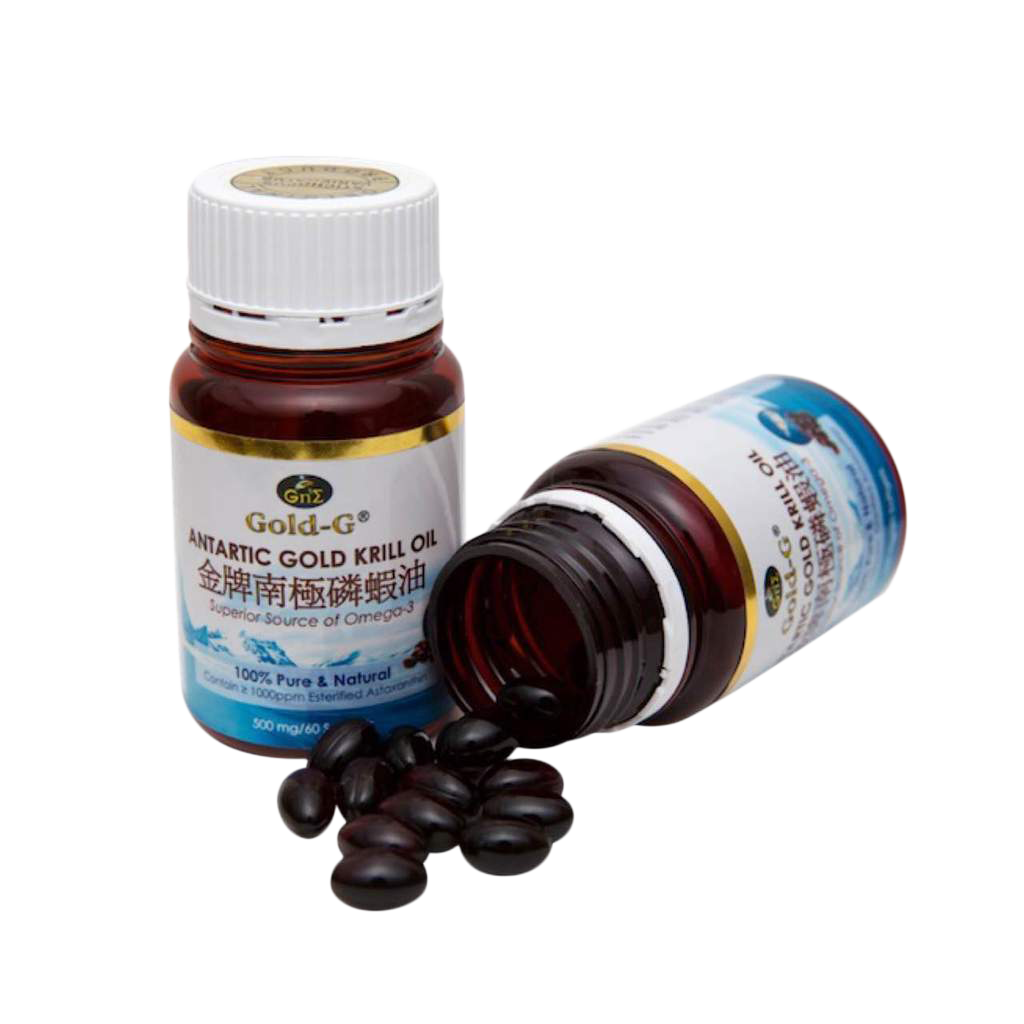
Gold-G® Antarctic Gold Krill Oil
Krill oil is an increasingly important source of omega-3 fatty acids specific for DHA and EPA. The fatty acids in krill oil are found in the form of phospholipid, which provides better bioavailability in terms of absorption and effectiveness. Besides, krill oil also contained a natural antioxidant, astaxanthin that could protect against oxidation and provide several health benefits.
- Omega-3 fatty acids promote wound healing by initiating tissue repair and reduce inflammation.
- Astaxanthin improves skin elasticity, skin texture and moisture content, rejuvenate skin, and reduce photoaging on skin.
Click the link below for direct purchase.
References
- America Cancer Society. (2020). Scars and Wounds. Retrieved from https://www.cancer.org/treatment/treatments-and-side-effects/physical-side-effects/skin-problems/scars-and-wounds.html
- Guo, S., & Dipietro, L. A. (2010). Factors affecting wound healing. Journal of dental research, 89(3), 219–229. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2903966/
- Mayo Clinic (2019). Cuts and scrapes: First aid. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-cuts/basics/art-20056711
- Mayo Clinic. (2018). First aid for burns. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-burns/basics/art-20056649
- Mickelson, M. A., Mans, C., & Colopy, S. A. (2016). Principles of Wound Management and Wound Healing in Exotic Pets. The veterinary clinics of North America. Exotic animal practice, 19(1), 33–53. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4663678/
- Office of Dietary Supplements – Iron. (2020). Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Iron-HealthProfessional/
- Office of Dietary Supplements – Selenium. (2020). Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Selenium-HealthProfessional/
- Office of Dietary Supplements – Vitamin C. (2020). Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-HealthProfessional/
- Office of Dietary Supplements – Zinc. (2020). Retrieved from https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Zinc-HealthProfessional/
- Quain, A. M., & Khardori, N. M. (2015). Nutrition in Wound Care Management: A Comprehensive Overview. Retrieved from https://www.woundsresearch.com/article/nutrition-wound-care-management-comprehensive-overview
- Wounds and Injuries | Fracture | Bruises. (2020). Retrieved from https://medlineplus.gov/woundsandinjuries.html
This website does not provide medical advice. The content of this website, such as graphics, images, text and all other materials, is provided for reference and educational purposes only. The content is not meant to be complete or exhaustive or to apply to any specific individual’s medical condition. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider regarding a medical condition.







